APRIL 3, 2003
Jupiter in the Hive
EXPLANATION
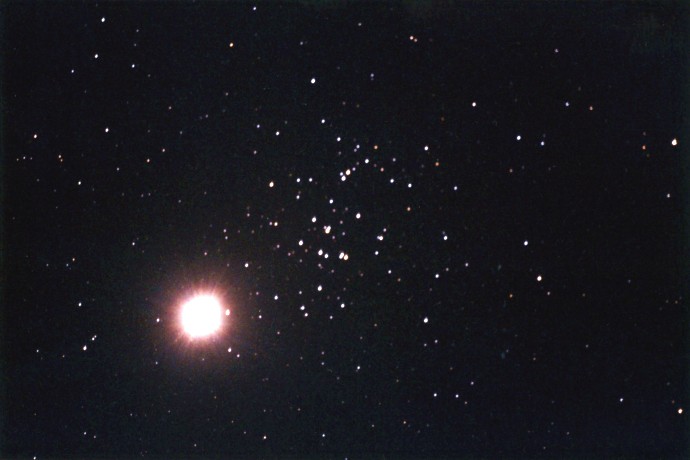
If you can find planet Jupiter in tonight’s sky, then you can also find M44, popularly known as the Beehive star cluster. In fact, with a pair of binoculars most casual skygazers should find it easy to zero in on this celestial scene. It should be easy because after sunset Jupiter presently rules the night as the brightest "star" overhead. Now near the stationary part of its wandering path through the heavens, Jupiter will obligingly linger for a while at a spot only a degree or so southeast of M44 in the relatively faint constellation Cancer. Seen here in a photograph from March 28, Jupiter (lower left) is strongly overexposed with the stars of M44 swarming above and to the right. The picture approximately corresponds to the view when looking through a typical pair of binoculars. Jupiter is about 30 light-minutes from our fair planet while M44, one of the closest star clusters, is around 600 light-years away.
Credit & Copyright