JULY 13, 2004
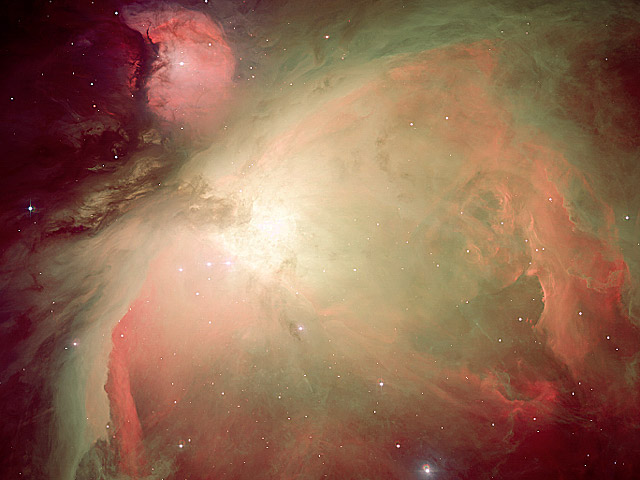
Orion Nebula in Oxygen, Hydrogen, and Sulfur
EXPLANATION
The Great Nebula in Orion, an immense, nearby starbirth region, is arguably the most famous of all astronomical nebulae. The Orion Nebula, also known as M42, is shown above through ultraviolet and blue filters augmented with three exact colors specifically emitted by hydrogen, oxygen, and sulfur. In addition to housing a bright open cluster of stars known as the Trapezium, the Orion Nebula contains many stellar nurseries. These nurseries contain glowing gas, hot young stars, proplyds, and stellar jets spewing material at high speeds. Many of the filamentary structures visible in this image are actually shock waves—fronts where fast moving material encounters slow moving gas. The Orion Nebula spans about 40 light years and is located about 1500 light years away in the same spiral arm of our Galaxy as the Sun.
Credit & Copyright