JANUARY 13, 2005
Infrared Trifid
EXPLANATION
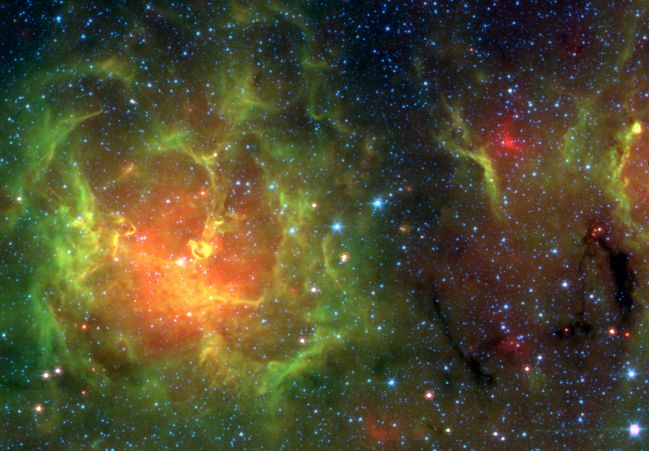
The Trifid Nebula, aka M20, is easy to find with a small telescope, a well known stop in the nebula rich constellation Sagittarius. But where visible light pictures show the nebula divided into three parts by dark, obscuring dust lanes, this penetrating infrared image reveals filaments of luminous gas and newborn stars. The spectacular false-color view is courtesy of the Spitzer Space Telescope. Astronomers have used the Spitzer infrared image data to count newborn and embryonic stars which otherwise can lie hidden in the natal dust and glowing clouds of this intriguing stellar nursery. As seen here, the Trifid is about 30 light-years across and lies only 5,500 light-years away.
Credit
J. Rho (SSC/Caltech), JPL-Caltech, NASA