MAY 27, 2006
Gamma-Ray Moon
EXPLANATION
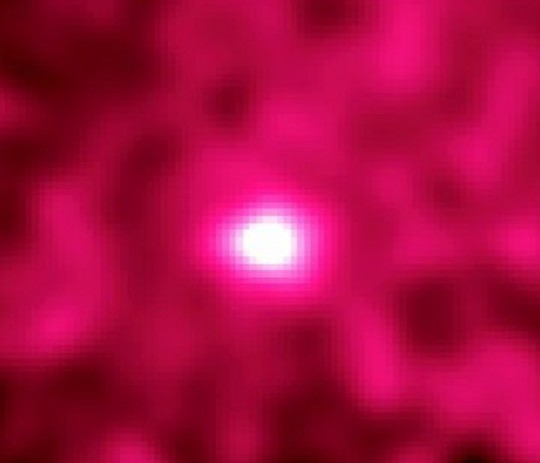
If you could see gamma rays—photons with a million or more times the energy of visible light—the Moon would appear brighter than the Sun! The startling notion is demonstrated by this image of the Moon from the Energetic Gamma Ray Experiment Telescope (EGRET) in orbit on NASA’s Compton Gamma Ray Observatory from April 1991 to June 2000. Then, the most sensitive instrument of its kind, even EGRET could not see the quiet Sun which is extremely faint at gamma-ray energies. So why is the Moon bright? High energy charged particles, known as cosmic rays, constantly bombard the unprotected lunar surface generating gamma-ray photons. EGRET’s gamma-ray vision was not sharp enough to resolve a lunar disk or any surface features, but its sensitivity reveals the induced gamma-ray moonglow. So far unique, the image was generated from eight exposures made during 1991-1994 and covers a roughly 40 degree wide field of view with gamma-ray intensity represented in false color.
Credit
Dave Thompson (NASA/GSFC) et al., EGRET, Compton Observatory, NASA