MAY 12, 2007
HD 189733b: Hot Jupiter
EXPLANATION
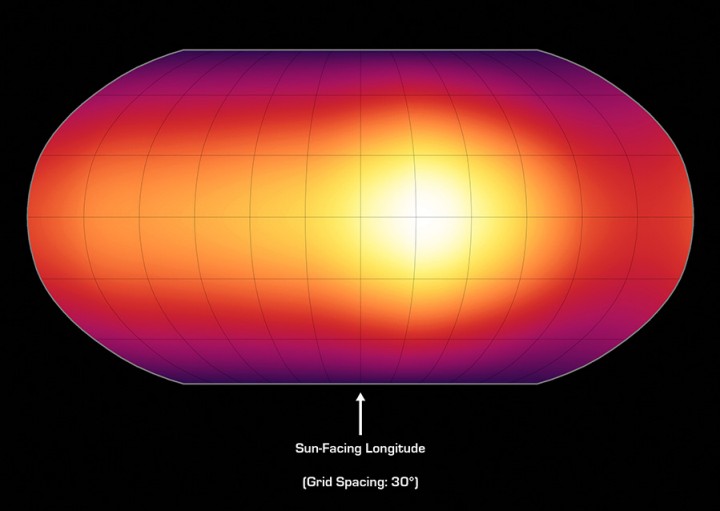
HD 189733b is a Jupiter-sized planet known to orbit a star some 63 light-years away. But while the distant world is approximately the size of Jupiter, its close-in orbit makes it much hotter than our solar system’s ruling gas giant. Like other detected hot Jupiters, its rotation is tidally locked—one side always faces its parent star as it orbits once every 2.2 days. Using infrared data from the Spitzer Space Telescope, this planet’s temperature variations have been mapped out -- the first map ever made for a planet beyond our solar system. Seen here (brighter colors = higher temperatures), the hottest spot on the planet is not at longitude 0.0, the point exactly facing the parent star. Instead, it’s about 30 degrees to the east (right), evidence that fierce, planet circling winds influence the temperature. In the planet-wide map, the temperature measurements vary from about 930 to 650 degrees C (1,700 to 1,200 F).
Credit
Heather Knutson (Harvard-Smithsonian CfA) et al., NASA / JPL-Caltech