FEBRUARY 7, 2009
Comet Lulin Tails
EXPLANATION
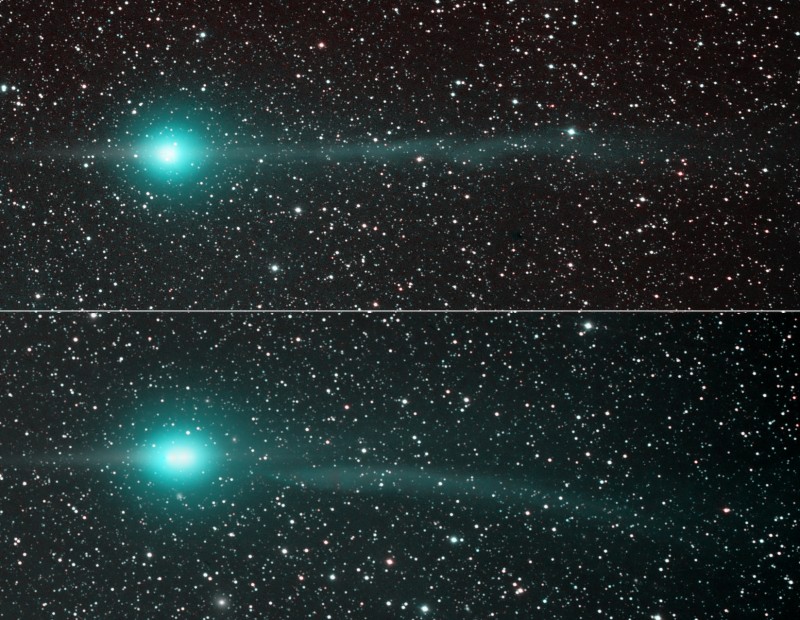
Sweeping through the inner solar system, Comet Lulin is easily visible in both northern and southern hemispheres with binoculars or a small telescope. Recent changes in Lulin’s lovely greenish coma and tails are featured in this two panel comparison of images taken on January 31st (top) and February 4th. Taken from dark New Mexico Skies, the images span over 2 degrees. In both views the comet sports an apparent antitail at the left—the comet’s dust tail appearing almost edge on from an earth-based perspective as it trails behind in Lulin’s orbit. Extending to the right of the coma, away from the Sun, is the beautiful ion tail. Remarkably, as captured in the bottom panel, Comet Lulin’s ion tail became disconnected on February 4, likely buffeted and torn away by magnetic fields in the solar wind. In 2007 NASA satellites recorded a similar disconnection event for Comet Encke. Don’t worry, though. Comet tails can grow back.
Credit & Copyright