SEPTEMBER 16, 2009
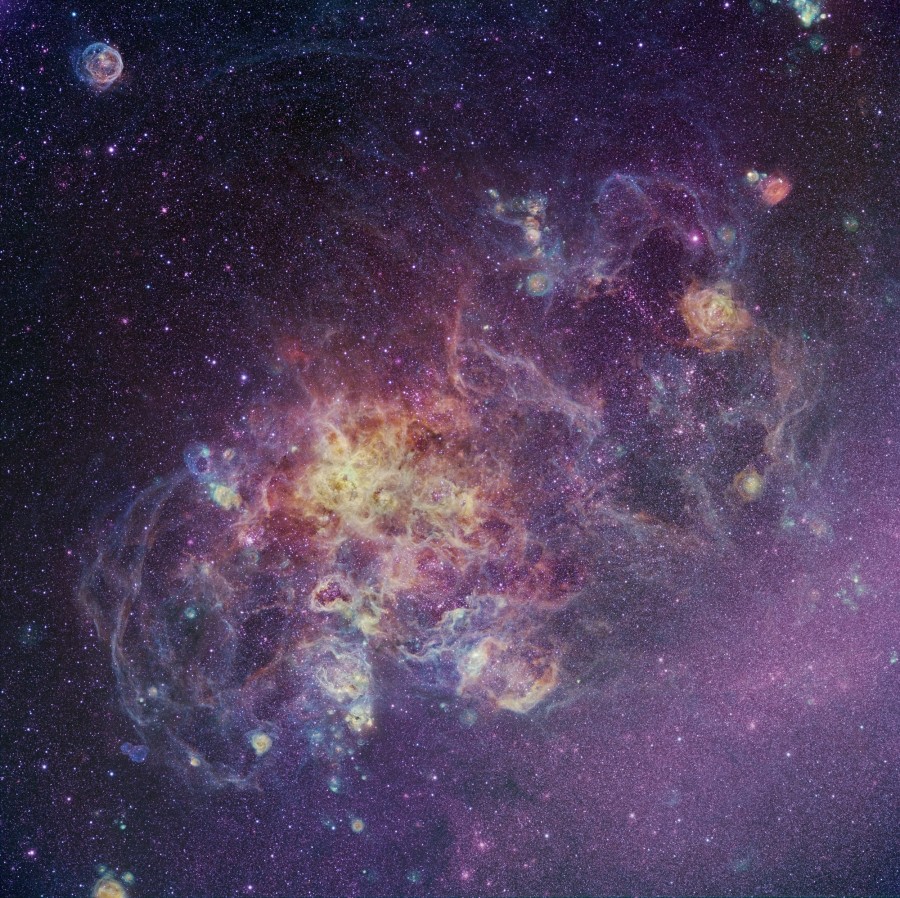
The Tarantula Zone
EXPLANATION
The Tarantula Nebula is more than 1,000 light-years in diameter—a giant star forming region within our neighboring galaxy the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC). That cosmic arachnid lies left of center in this sharp, colorful telescopic image taken through narrow-band filters. It covers a part of the LMC over 2,000 light-years across. Within the Tarantula (NGC 2070), intense radiation, stellar winds and supernova shocks from the central young cluster of massive stars, cataloged as R136, energize the nebular glow and shape the spidery filaments. Around the Tarantula are other violent star-forming regions with young star clusters, filaments and bubble-shaped clouds. The rich field is about as wide as the full Moon on the sky, located in the southern constellation Dorado.
Credit & Copyright