FEBRUARY 3, 2012
Inside the Eagle Nebula
EXPLANATION
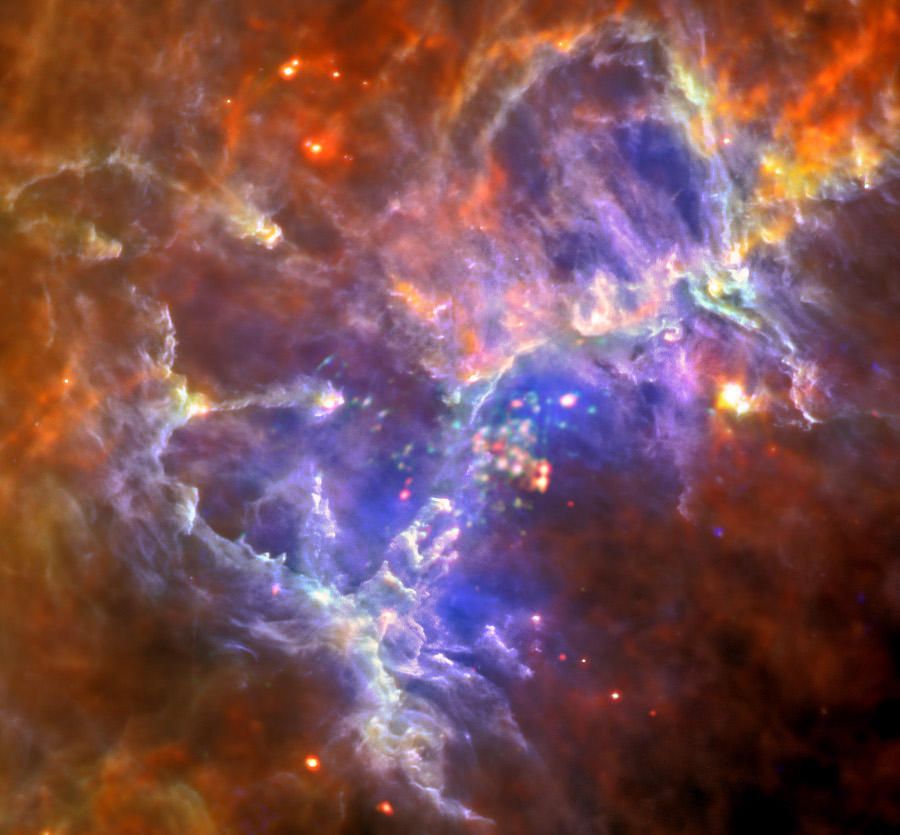
In 1995, a now famous picture from the Hubble Space Telescope featured Pillars of Creation, star forming columns of cold gas and dust light-years long inside M16, the Eagle Nebula. This remarkable false-color composite image revisits the nearby stellar nursery with image data from the orbiting Herschel Space Observatory and XMM-Newton telescopes. Herschel’s far infrared detectors record the emission from the region’s cold dust directly, including the famous pillars and other structures near the center of the scene. Toward the other extreme of the electromagnetic spectrum, XMM-Newton’s X-ray vision reveals the massive, hot stars of the nebula’s embedded star cluster. Hidden from Hubble’s view at optical wavelengths, the massive stars have a profound effect, sculpting and transforming the natal gas and dust structures with their energetic winds and radiation. In fact, the massive stars are short lived and astronomers have found evidence in the image data pointing to the remnant of a supernova explosion with an apparent age of 6,000 years. If true, the expanding shock waves would have destroyed the visible structures, including the famous pillars. But because the Eagle Nebula is some 6,500 light-years distant, their destruction won’t be witnessed for hundreds of years.
Credit
Far-infrared:
ESA/Herschel/PACS/SPIRE/Hill, Motte, HOBYS Key
Programme Consortium;
X-ray:
ESA/XMM-Newton/EPIC/XMM-Newton-SOC/Boulanger